Joined September 2024
- Tweets 87,411
- Following 405
- Followers 401
- Likes 73,244
Pinned Tweet
لا يمكن شراؤنا ولنا شرف. كن حذرًا من الناس - الذين لا يستطيعون شراء كل شيء إلا بالمال ويخونونك. العب لعبة مزدوجة، إذا جاز التعبير.
Frauen gibt es überall 😉 - sollte man sich nicht ködern lassen. Ich suche eher Business bzw. rechte Hand.
Hänge ich wie immer ab. Ich kenne Viele die ihre Internetplattformen und Millionen bis milliardenschweren Firmen haben - aber leider kein Highschool. Die haben alles abgehängt.
Broschüren kann ich auch für Direktmarketing erstellen. Die lassen sich über eigene gute Drucker oder auch über Dienste in Hochglanz oder Matt drucken.
Serienbriefe eignen sich für Marketing, da sie durch Personalisierung die Aufmerksamkeit erhöhen, Zeit sparen und eine konsistente Kommunikation fördern. Sie werden für personalisierte Angebote, Kampagnen oder Einladungen verwendet.
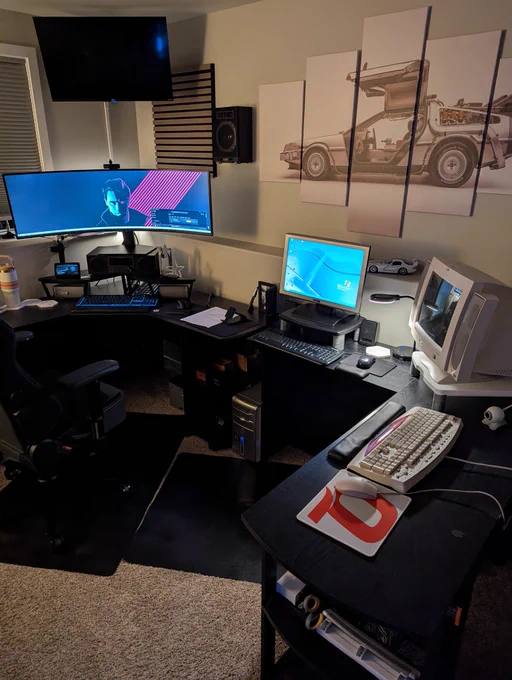
Nicht so billig - sondern Hightech-Labor im grauen Stil mit paar Tausend Deutsche Mark Schreibtisch und passenden Schrank für Elektronik, die neueste Hardware, erste professionelle Websites besser, Netzwerk. Ziemlich hochwertig.
Bei mir sah es aus wie ein Hightech Labor mit teuren Möbeln, statt billige Spiele-Computer. Dazu halt der ganze Hightech mit zusätzlichen Geräten für Satellit, 🛰️ und Lötstationen, Messgeräten, speziellen Netzteilen, Oszillator
Vergangenheiten kann man nicht ändern.
Gibt es auch eine Alternative dazu - aber hat man immer gerne verwendet.
Let's talk about - Redis
But first, make sure you’re following @techNmak
➸ Redis wasn't born in a lab – it was born from frustration. 😉
How?
➸ Back in 2009, Salvatore Sanfilippo needed a faster way to analyze website traffic for his startup.
Existing databases just couldn't keep up.
➸ So, he built his own solution => Redis (a super-fast data store that lives in your computer's memory.)
It was a game-changer, and it's still transforming how we handle data today.
📌 𝐋𝐞𝐭'𝐬 𝐮𝐧𝐝𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐢𝐧 𝐝𝐞𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐥.
Redis => REmote DIctionary Server
◾ initially designed to be a remote data structure server accessible over the network.
◾ open-source, in-memory data store.
◾ functions mainly as a key-value database
◾ but goes beyond by offering a variety of data structures like strings, lists, sets, sorted sets, hashes etc.
◾ primarily resides in RAM, providing incredibly fast read and write operations.
◾ options for persistence to disk, ensuring data durability.
𝐑𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐬 𝐟𝐚𝐬𝐭. 𝐖𝐡𝐲?
As we discussed,
Unlike traditional databases that primarily store data on disk, Redis keeps its entire dataset in memory (RAM).
This eliminates the latency associated with disk seeks and reads, allowing for very fast data access.
📌 𝐑𝐄𝐒𝐏 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐜𝐨𝐥 => REdis Serialization Protocol
◾ Redis uses its own binary-safe protocol called RESP for communication.
- designed for simplicity and efficiency
- less overhead as compared to text-based protocols like HTTP
📌 𝐄𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐋𝐨𝐨𝐩 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐈/𝐎 𝐌𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱𝐢𝐧𝐠
◾ The heart of Redis => event loop. (single-threaded)
◾ continuously monitors file descriptors (sockets) for client connections and incoming commands.
◾ event-driven architecture, combined with I/O multiplexing (epoll, kqueue, or select) => allows Redis to handle thousands of concurrent clients efficiently without the overhead of multiple threads.
◾ non-blocking I/O operations
- not waiting for I/O operations to complete
- main thread remains responsive and can quickly process other commands
◾ if main thread encounters a time-consuming operation (like accessing the disk or network), it doesn't halt and wait => delegates the task to the operating system and registers a callback function to be executed once the operation completes.
📌 𝐌𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐅𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐣𝐞𝐦𝐚𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐜
◾ Redis uses a memory allocator called jemalloc to manage memory efficiently.
◾ Jemalloc helps reduce memory fragmentation, which can occur when objects are allocated and freed repeatedly.
📌 𝐑𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐬 𝐨𝐟𝐟𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐯𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐝𝐞𝐩𝐥𝐨𝐲𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐦𝐨𝐝𝐞𝐬.
◾ Standalone - A single instance of Redis.
◾ Cluster - A distributed implementation for scalability and high availability.
◾ Sentinel - High availability for standalone or replicated Redis instances.
◾ Replication - Master-replica setup for data redundancy and read scalability.
DIY: Create Your Own Cloud with Kubernetes (Part 1)
kubernetes.io/blog/2024/04/0…
Gnome ist ein cooles Projekt für Linux (neben KDE und Xfce). Ich würde weg vom Klassischen mit Icons.
release.gnome.org/49/
Rethinking Window Management
blogs.gnome.org/tbernard/202…
3D Diagramme Kreisdiagramme, Balkendiagramme mit StarDivsion StarOffice
Kalkulationen - verwende ich gerne die Kalkulationsprogramme. Dann auch mit Microsoft Excel, aber auch für die Erstellung von tausenden Serienbriefen im Grunde auch personalisiert.
Schon mit Windows 95
Was wir früher noch auf Papier gemacht machen, haben wir früh genug auf Computer mit IBM Spracherkennung ViaVoice unter Windows 95 gemacht. Das war für mich bereits Zukunft. Mich mit Stab-Mikrofon. Gamer hatten spezielle Kopfhörer mit Mikrofon. Bei denen war wohl Sennheiser in
Meine Mutter hatte auch immer
Mein Gott
Oh mein Gott
Gott sei Dank
verwendet. Fand man witzig.
"اللَّهُمَّ #صَباحًا مُبَارَكًا تُزهِرُ فِيهِ الآمَالُ، وَتَتَنَفَّسُ فِيهِ الأَرْوَاحُ طُمَأْنِينَةً وَرِضًا، وَتَكْتُبُ لَنَا فِيهِ كُلَّ خَيْرٍ وَسَعَادَةٍ
#صباح_الخير
#صباح_الخير_والسعاده