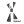My actual focus : practical agentic workflows as in "useful for business" Some older ones : strategy, neuro, geopol, MLAI, intelligence, etc.
Europe
Joined April 2024
- Tweets 9,074
- Following 702
- Followers 499
- Likes 19,257
Hope = Interesting work 👇
As usual, I like the neuro-inspired works from Deep Mind in general (check Titans & Miras for example)
Continual learning is one of the critical feature in the near future.
(as is surprise vs expectations by the way imho...)
Google introduces Nested Learning, "a new ML paradigm for continual learning":
"Nested Learning... represents a step forward in our understanding of deep learning. By treating architecture and optimization as a single, coherent system of nested optimization problems, we unlock a new dimension for design, stacking multiple levels.
We believe the Nested Learning paradigm offers a robust foundation for closing the gap between the limited, forgetting nature of current LLMs and the remarkable continual learning abilities of the human brain."
Interesting work here (as was already Titans from the same authors imo) 👇
I'm glad to see more "neuro inspired" integration works recently.
Bravo to the team 👏👏
Introducing Nested Learning: A new ML paradigm for continual learning that views models as nested optimization problems to enhance long context processing. Our proof-of-concept model, Hope, shows improved performance in language modeling. Learn more: goo.gle/47LJrzI
@GoogleAI
Interesting take here 👇
Imho = AI Expansion is much more interesting than AI Augmentation (mostly transaction cost driven) ... Or AI Automation (simple mimicking of current human workflows)
In 5 years from now, probably 95% of the tokens used by AI agents will be used on tasks that humans never did before.
I just met with about 30 enterprises across 2 days and a dinner, and some of the most interesting use-cases that keep coming up for AI agents are on bringing automated work to areas that the companies would not have been able to apply labor to before.
Most of the world hasn’t quite caught on to this point yet. We imagine AI as dropping into today’s workflows and just taking what we already do and making it more efficient by 20% or something. Yet most companies realize that most of the time they’re doing far less than they could because of the cost or limited capacity of talent.
This shows up in different ways across every industry. In real estate it’s ideas like being able to read and analyze every lease agreement for every trend and business opportunity possible. In life sciences it’s being able to rapidly do drug discovery or improve quality by looking through errors in data. In financial services it’s being able to look through all past deals and figure out better future monetization. In legal it’s being able to execute on contracts or legal work for previously unprofitable segments or projects.
And these are just the Box AI use cases that deal with documents and content. The same is going to be true in coding, where companies tackle software projects they wouldn’t have done before. Security of all systems and events they couldn’t get to. And so on.
If you are working on AI Agents right now, the big opportunity is to bring enterprises “work” for problems that they couldn’t do before because it was nearly impossible to afford or scale.
And if you’re deploying AI agents in an enterprise, consider what things you’d do more of (or differently) if the cost and speed of labor became 100X cheaper and faster. This is going to get you the real upside of automation.
Good paper.
No real surprises here imo. But finally a serious paper on the topic of synthetic reasoning 👇
Can LLM agents learn by dreaming? 🌙🤖
DreamGym from Meta is a new framework that lets AI agents train via synthetic reasoning-based experiences instead of costly real rollouts. It models environment dynamics, replays and adapts tasks, and even improves sim-to-real transfer.
Results: +30% gains on WebArena and PPO-level performance—using only synthetic interactions.
GEMs = Very interesting work here imo on human behaviors simulation 👇
Curious to know to what others use cases we can apply this one ... (testing time for some ideas lol)
Bravo to the team ! 👏 And thanks for the pointer @JosephJSSuh
LLMs have dominated recent work on simulating human behaviors. But do you really need them?
In discrete‑choice settings, our answer is: not necessarily.
A lightweight graph neural network (GNN) can match or beat strong LLM-based methods.
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2511.02135 🧵👇
Nice 👇
I've built a branch of TRM that provides cleaner experimentation and training on a simple problem (Sudoku 4x4). This allows anyone to debug/understand/experiment with TRM rapidly. @jm_alexia
github.com/olivkoch/TinyRecu…
Cool work 👇
There’s lots of symmetry in neural networks!
🔍 We survey where they appear, how they shape loss landscapes and learning dynamics, and applications in optimization, weight space learning, and much more.
➡️ Symmetry in Neural Network Parameter Spaces arxiv.org/abs/2506.13018
We need more domain expertise specialized dataset like ReasonMed imho 👇
Cool work ! Bravo to the team 👏👏
ReasonMed: the largest medical reasoning dataset, advancing LLM performance in clinical QA.
Comprising 370k curated examples distilled from 1.75M reasoning paths, ReasonMed is built through a multi-agent EMD (easy–medium–difficult) pipeline with generation, verification, and an Error Refiner that corrects faulty reasoning steps.
Experiments show that combining detailed CoT reasoning with concise answer summaries yields the most robust fine-tuning outcomes.
- Models trained on ReasonMed redefine the state of the art:
- ReasonMed-7B outperforms all sub-10B models by +4.17% and even beats LLaMA3.1-70B on PubMedQA (+4.60%).
- ReasonMed-14B maintains strong scaling efficiency and competitive accuracy.
ReasonMed: A 370K Multi-Agent Generated Dataset for Advancing Medical Reasoning
Alibaba DAMO Academy, Lanzhou, and others
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2506.09513
Hugging Face: huggingface.co/datasets/ling…
Code: github.com/alibaba-damo-acad…
Our report: mp.weixin.qq.com/s/KU43grtdT…
📬 #PapersAccepted by Jiqizhixin
👇
Diffusion Language Models are Super Data Learners
"when unique data is limited, diffusion language models (DLMs) consistently surpass autoregressive (AR) models by training for more epochs."
"At scale, a 1.7B DLM trained with a ∼ 1.5T - token compute budget on 10B unique Python tokens overtakes an AR coder trained with strictly matched settings. In addition, a 1B-parameter DLM achieves > 56% accuracy on HellaSwag and > 33% on MMLU using only 1B tokens, without any special tricks, just by repeating standard pre-training data."
MemSearcher = interesting work here 👇
Finally beyond ReAct and simple scratchpad (practitioners have been doing this for months... imho)
Check the compressive memory & more critically the recursive/difference updater
Bravo to the team ! 👏
Can wait to test the code /models
MemSearcher trains LLM search agents to keep a compact memory, boosting accuracy and cutting cost.
Most agents copy the full history, bloating context and slowing inference, but MemSearcher keeps only essential facts.
Each turn it reads the question and memory, then searches or answers.
After reading results, it rewrites memory to keep only what matters.
This holds token length steady across turns, lowering compute and GPU use.
Training uses reinforcement learning with Group Relative Policy Optimization.
Their variant shares a session reward across turns, teaching memory, search, and reasoning together.
Across 7 QA benchmarks it beats strong baselines, with 3B surpassing some 7B agents.
It uses fewer tokens than ReAct, so long tasks stay efficient and reliable.
----
Paper – arxiv. org/abs/2511.02805
Paper Title: "MemSearcher: Training LLMs to Reason, Search and Manage Memory via End-to-End Reinforcement Learning"
👇
1. OpenAI expects to end the year at a $20B annualized revenue run rate.
2. There is an "upcoming enterprise offering".
3. "Given everything we see on the horizon in our research program, this is the time to invest to be really scaling up our technology [i.e., data center infrastructure]."
4. A world where AI can make important scientific breakthroughs at the cost of tremendous amounts of computing power is something OpenAI "no longer think[s] is in the distant future".
👇
🚀 Hello, Kimi K2 Thinking!
The Open-Source Thinking Agent Model is here.
🔹 SOTA on HLE (44.9%) and BrowseComp (60.2%)
🔹 Executes up to 200 – 300 sequential tool calls without human interference
🔹 Excels in reasoning, agentic search, and coding
🔹 256K context window
Built as a thinking agent, K2 Thinking marks our latest efforts in test-time scaling — scaling both thinking tokens and tool-calling turns.
K2 Thinking is now live on kimi.com in chat mode, with full agentic mode coming soon. It is also accessible via API.
🔌 API is live: platform.moonshot.ai
🔗 Tech blog: moonshotai.github.io/Kimi-K2…
🔗 Weights & code: huggingface.co/moonshotai
Agent B retweeted
Open AI today:
'Although the potential upsides are enormous, we treat the risks of superintelligent systems as potentially catastrophic and believe that empirically studying safety and alignment can help global decisions, like whether the whole field should slow development to more carefully study these systems as we get closer to systems capable of recursive self-improvement.'
ThoughtCom = Very interesting paper here imo 👇
Some seriously interesting approaches here.
Would love to see a repo on this one.
Bravo to the team @YujiaZheng9 ! 👏👏
🧠 What if large models could read each other’s minds?
Our new paper (#neurips2025 spotlight), “Thought Communication in Multiagent Collaboration”, explores how large model agents can share latent thoughts, not just messages.
📷arxiv.org/abs/2510.20733 (CMU × Meta AI × MBZUAI)
Imagine teams of agents that don’t just talk, but directly read each other’s minds during collaboration. That’s the essence of Thought Communication, which goes beyond the fundamental limits of natural language, or any observed modalities.
🧩 Theoretically, we prove that in a general nonparametric setting, both shared and private latent thoughts can be identified from model states under a sparsity regularization.
Our theory ensures these recovered representations reflect the true internal process of agent reasoning, and that the causal structure between agents and their thoughts can be reliably recovered.
⚙️ Practically, we introduce ThoughtComm, a general framework for latent thought communication. Guided by the theory, we implement a sparsity-regularized autoencoder to extract thoughts from model states and infer which are shared or private.
This lets agents not only know what others are thinking, but also which thoughts they mutually hold or keep private — a step toward real collective intelligence.
Across diverse models, communication beyond language directly enhances coordination, reasoning, and collaboration among LLM agents.
🔮 In line with recent studies, we believe this work further highlights the importance of the hidden world underlying foundation models, where understanding thought, not just observational behavior, becomes central to intelligence.
#MultiAgent #LLMs #Causality #AI #ML
Joint work with @zhuokaiz @ Zijian Li @xie_yaqi @ Mingze Gao @LizhuZhang @kunkzhang
Interesting guide here 👇
Leveraging similar ideas than Anthropic skills (progressive disclosure, and so on)
Anthropic just posted another banger guide.
This one is on building more efficient agents to handle more tools and efficient token usage.
This is a must-read for AI devs!
(bookmark it)
It helps with three major issues in AI agent tool calling: token costs, latency, and tool composition.
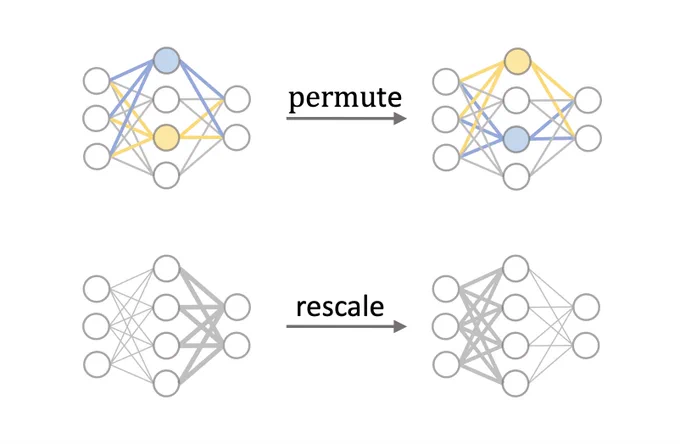
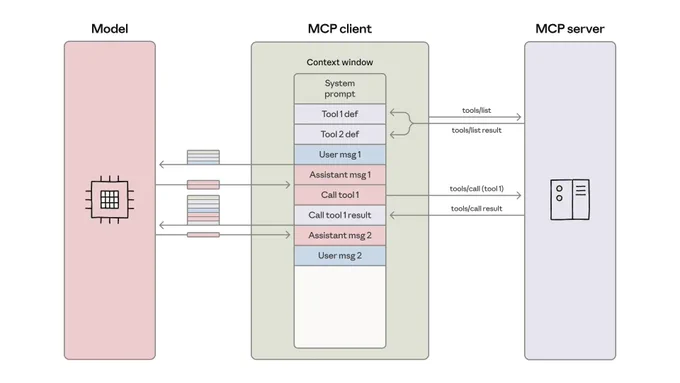
How? It combines code executions with MCP, where it turns MCP servers into code APIs rather than direct tool calls.
Here is all you need to know:
1. Token Efficiency Problem: Loading all MCP tool definitions upfront and passing intermediate results through the context window creates massive token overhead, sometimes 150,000+ tokens for complex multi-tool workflows.
2. Code-as-API Approach: Instead of direct tool calls, present MCP servers as code APIs (e.g., TypeScript modules) that agents can import and call programmatically, reducing the example workflow from 150k to 2k tokens (98.7% savings).
3. Progressive Tool Discovery: Use filesystem exploration or search_tools functions to load only the tool definitions needed for the current task, rather than loading everything upfront into context. This solves so many context rot and token overload problems.
4. In-Environment Data Processing: Filter, transform, and aggregate data within the code execution environment before passing results to the model. E.g., filter 10,000 spreadsheet rows down to 5 relevant ones.
5. Better Control Flow: Implement loops, conditionals, and error handling with native code constructs rather than chaining individual tool calls through the agent, reducing latency and token consumption.
6. Privacy: Sensitive data can flow through workflows without entering the model's context; only explicitly logged/returned values are visible, with optional automatic PII tokenization.
7. State Persistence: Agents can save intermediate results to files and resume work later, enabling long-running tasks and incremental progress tracking.
8. Reusable Skills: Agents can save working code as reusable functions (with SKILL .MD documentation), building a library of higher-level capabilities over time.
This approach is complex and it's not perfect, but it should enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your AI agents across the board.
anthropic. com/engineering/code-execution-with-mcp
Interesting work here 👇
The paper explains how to make AI decisions clear and easy to audit.
It defines transparency as seeing how a system works and interpretability as understanding why one result happened.
Adds 2 practical ideas, marginal transparency and marginal interpretability, which say extra detail helps less over time.
It reviews simple add-on explainers for black-box models, like LIME for local behavior and SHAP for fair feature credit.
Also covers models that are already clear, like decision trees and purpose-built neural networks that highlight key inputs.
Organizes methods by when and what they explain, before training or after, local cases or global behavior.
Also warns that explanations can leak private data and lists privacy-preserving ways to share only safe signals.
mdpi. com/2673-2688/6/11/285
Live benchmarks are highly useful for serious agents imho.
Why ? = a lot of knowledge work has a contact surface with fast-changing/pacing InfoSpaces...
Bravo to the team ! 👏👏
Here applied to trading 👇
Can LLMs handle real-world uncertainty, not just static tests?
LiveTradeBench introduces the first live trading benchmark for LLM agents—evaluating decision-making in evolving markets rather than fixed datasets. It streams real market prices and news, supports multi-asset portfolio management, and spans U.S. stocks and Polymarket for diverse environments.
In 50-day live trials of 21 models, results reveal that benchmark scores don’t predict trading success, LLMs exhibit distinct portfolio behaviors, and a few can adapt to real-time signals—highlighting a new frontier for dynamic LLM evaluation.
LiveTradeBench: Seeking Real-World Alpha with Large Language Models
University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign
Project: trade-bench.live
Code: github.com/ulab-uiuc/live-tr…
Paper: trade-bench.live/assets/live…
Our report: mp.weixin.qq.com/s/4cyUC8jdR…
📬 #PapersAccepted by Jiqizhixin
Interesting podcast imo
A lot of food for thoughts inside this one = an example 👇
My excellent Conversation with Sam Altman: conversationswithtyler.com/e…, @sama