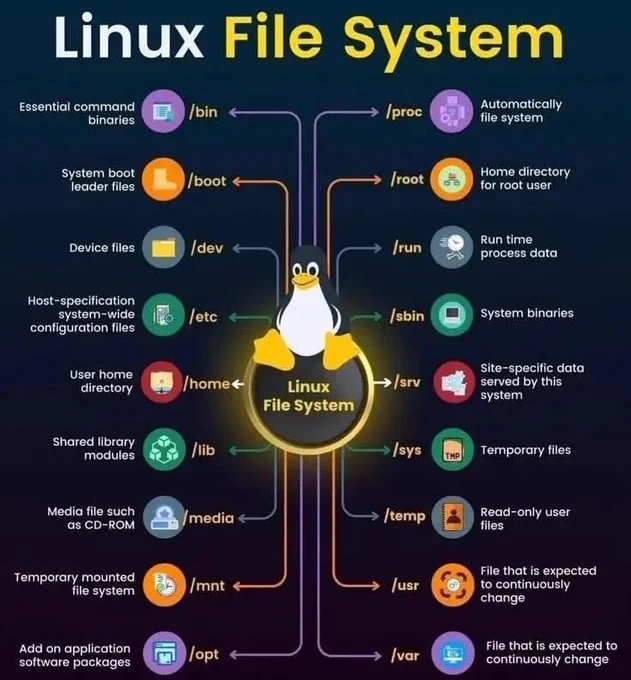
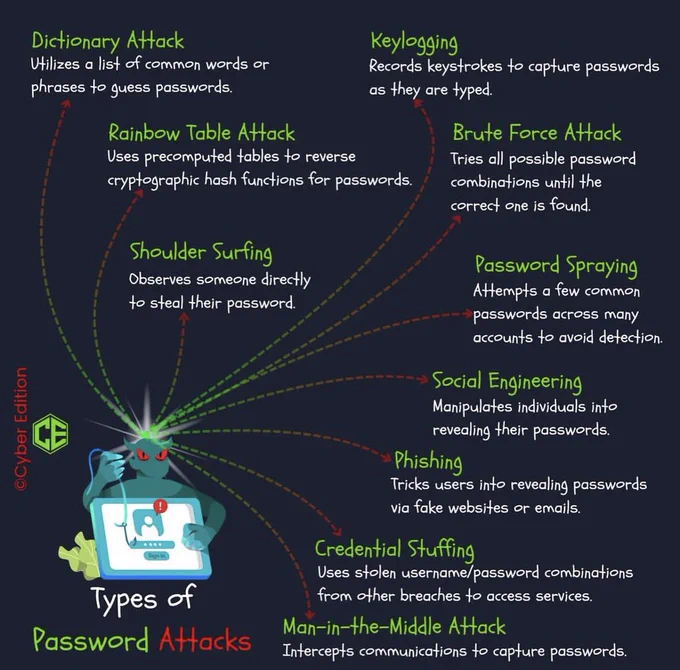
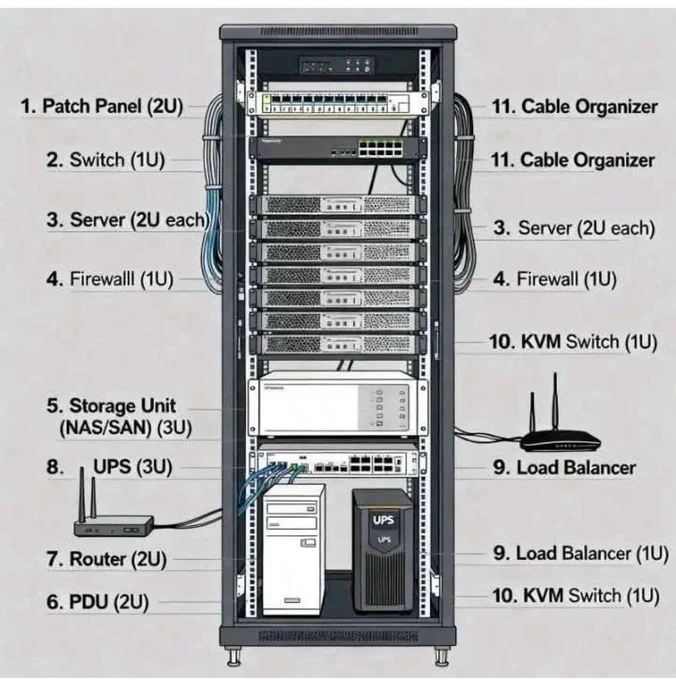
Networking CheatSheet!! | IPCisco
.
✨✨%60 off blackfriday coupon: udemy.com/course/ccna-200-30…
.
#ccna #BlackFriday #cisco
Amir Khan retweeted
Docker Containers vs Virtual Machines
→ Both Docker containers and Virtual Machines (VMs) are technologies used to isolate applications and their environments.
→ While they serve similar purposes, they differ significantly in structure, performance, and resource utilization.
→ Understanding these differences helps developers choose the right tool for application deployment and scalability.
What Are Containers?
→ Containers are lightweight, portable units that package an application and its dependencies.
→ They share the host operating system’s kernel, allowing multiple containers to run on the same OS without needing separate OS instances.
→ Docker containers start almost instantly and use minimal system resources.
What Are Virtual Machines?
→ Virtual Machines emulate entire operating systems.
→ Each VM runs on a hypervisor, which virtualizes hardware resources for multiple guest OS instances.
→ Every VM includes its own OS kernel, making it heavier and slower to start compared to containers.
Architecture Comparison
→ Containers Architecture:
• Runs on the host OS using Docker Engine or another container runtime.
• Shares the OS kernel among all containers.
• Uses layered images for efficient storage and deployment.
→ Virtual Machines Architecture:
• Runs on a hypervisor (e.g., VMware, VirtualBox, KVM).
• Each VM has its own OS, virtualized hardware, and application stack.
• Requires more disk space and memory to operate.
Performance Differences
→ Containers are lightweight and can start in seconds due to shared kernel architecture.
→ VMs take longer to boot since they load a full OS.
→ Containers consume fewer system resources, while VMs demand more CPU and memory.
Isolation and Security
→ Containers provide process-level isolation, meaning they share the host OS kernel but run in separate user spaces.
→ VMs provide full isolation, each running its own OS, which offers stronger security boundaries but at higher cost.
Portability and Deployment
→ Containers are highly portable — an image built on one system can run anywhere Docker is supported.
→ VMs are less portable due to their dependency on hypervisor configurations and full OS setups.
→ Containers are ideal for microservices, while VMs are suited for running different OS environments.
Resource Efficiency
→ Containers require fewer resources since they reuse the host’s kernel.
→ VMs duplicate OS kernels, increasing storage and memory usage.
→ A single host can run dozens of containers but only a few VMs efficiently.
Use Cases
→ Containers:
• Microservices architecture
• Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
• Cloud-native and scalable applications
→ Virtual Machines:
• Running applications requiring different OS environments
• Legacy systems
• Full isolation for security-critical workloads
Quick tip
→ Docker containers and Virtual Machines both provide isolated environments but with different levels of abstraction.
→ Containers are faster, more efficient, and portable — ideal for modern, cloud-native development.
→ VMs offer stronger isolation and flexibility for running different operating systems.
→ The choice depends on the project’s scalability, security, and environment requirements.
Get the Docker Playbook here:
codewithdhanian.gumroad.com/…
Amir Khan retweeted
Do you want to become a hacker? You're gonna need a virtual machine.
Here's everything you need to know about virtual machines and how to set them up yourself.
Watch now 👉 piped.video/watch?v=wX75Z-4M…
Amir Khan retweeted
Amir Khan retweeted
My System Design - Cheat sheet
System design is about creating applications that can handle real-world demands.
𝐒𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐃𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬
📌 𝐍𝐞𝐭𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠
DNS - Domain Name System (resolvers, nameservers, records)
Load Balancers - Hardware, software, Layer 4, Layer 7
CDNs - Content Delivery Networks (caching, edge servers)
Proxies - Forward, reverse, transparent, anonymous
VPNs - Virtual Private Networks (tunneling protocols)
Firewalls - Packet filtering, stateful inspection
NAT - Network Address Translation
Gateways - Connect different networks
Routers - Direct traffic between networks
📌 𝐒𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐞
Databases - SQL, NoSQL (key-value, document, columnar, graph), NewSQL
Object Storage - Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage
Block Storage - Network-attached storage (NAS), storage area networks (SAN)
File Systems - Distributed file systems (HDFS, Ceph), Network File System (NFS)
Caching - Redis, Memcached, Varnish, CDN edge caches
📌 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐮𝐭𝐞
Servers - Bare metal, virtual machines (VMs)
Containers - Docker, Kubernetes, container orchestration
Serverless - AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions
FaaS - Function-as-a-Service
PaaS - Platform-as-a-Service
📌 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
APIs - REST, GraphQL, SOAP, gRPC
Message Queues - RabbitMQ, Kafka, ActiveMQ, Amazon SQS
WebSockets - Real-time, full-duplex communication
RPC - Remote Procedure Call, XML-RPC, JSON-RPC
Pub/Sub - Publish-subscribe messaging pattern
Service Mesh - Istio, Linkerd
📌 𝐀𝐫𝐜𝐡𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐏𝐚𝐭𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐧𝐬
Microservices - Domain-driven design (DDD), service discovery, API gateways
Monolithic - Layered architecture, MVC, MVP
Event-driven - Event sourcing, CQRS
Serverless - FaaS, BaaS (Backend-as-a-Service)
📌 𝐒𝐜𝐚𝐥𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲 & 𝐑𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲
Horizontal Scaling - Load balancers, auto-scaling groups
Vertical Scaling - Larger instances, more resources
Replication - Master-slave, master-master
Sharding - Partitioning data across multiple databases
Redundancy - Multiple instances, failover mechanisms
Fault Tolerance - Graceful degradation, circuit breakers
Disaster Recovery - Backups, replication, geo-redundancy
📌 𝐒𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲
Authentication - Multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), OAuth, OpenID Connect
Authorization - Role-based access control (RBAC), Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
Encryption - Symmetric, asymmetric, hashing algorithms
Security Protocols - TLS/SSL, HTTPS, SSH
Web Application Firewalls (WAF) - Protect against web attacks
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) - Identify malicious activity
📌 𝐎𝐛𝐬𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲
Monitoring - Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog, New Relic
Logging - ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Splunk
Tracing - Distributed tracing (Jaeger, Zipkin)
Metrics - Counters, gauges, histograms, summaries
APM - Application Performance Monitoring (Dynatrace, AppDynamics)
📌 Follow - @techNmak
FREE hosting:
🟣 Sevalla․com
🐙 GitHub Pages
🚀 Netlify
⚡ Vercel
☁️ Cloudflare Pages
🦊 GitLab Pages
🔥 Firebase Hosting
🧭 AWS Amplify
🛠️ Render
🌊 Surge
🌟 Gatsby Cloud
🏝️ Neocities․org
📦 FreeHosting
♾ InfinityFree
0️⃣ Static․run
🏆 AwardSpace
🧵 Byet Host
🧭 Bitbucket